 Chemistry - Carbon 1 Chemistry - Carbon 1
| Carbon - one of the most important foundations of life |
Normal people have direct contact with carbon, e.g. with pencil leads, and perceive it as a rather soft, slightly lubricating material. Somewhat richer people come with a diamond in touch, in contrast to graphite very hard.
As the smallest particles, diamonds are considered the high-end solution for abrasives.
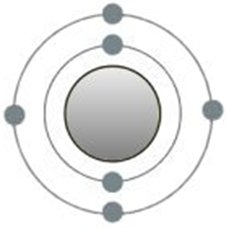
Using the example of the carbon atom (lat. carbo - coal), bonds between the atoms can be analysed more precisely in order to understand the formation of molecules. It is interesting because there are four possible
chemical bonds. Above it is shown with its six electrons according to the shell model. Afterwards on the second shell exactly these four places remain for completion.
| Carbon - founder of inorganic chemistry |
An atom can use several possibilities for bonds differently, either to different other atoms or to the same atom. An example of the latter would be oxygen, which binds to another oxygen atom with a total of only two
bonds. Of course, carbon has more possibilities. If it uses all four bonds to form atoms of the same type, it produces diamond that is hard to beat.
| carbon - a solid non-metallic material |
Of course there are many more possibilities with four bonds than with two with oxygen or one with hydrogen. Carbon e.g. can form the famous benzol ring or chain with six atoms. There are still options for
reinforcements between chains. If there are many, high-octane fuel is produced, if there are fewer diesel engines. The technology used to create a large number of new products is also called carbon chemistry.
There is the cinematic representation of the case in which all carbon or better plastic products would be taken from us. There is not much left in normal habitats. In a car it would be similar. Although metals still play an
important role in terms of weight, plastics have a high volume share due to their low weight. By the way, because of the synthetic fibres it's not clear from this experiment what we're going to end up wearing anything of
cloth.
First, we look at how carbon affects the properties of steel. In our ears we still hear the sentence: 'Steel is all iron material with a carbon content not exceeding 1.5 percent that can be forged without post-treatment.'
Today we speak of a carbon mass fraction of at most 2 percent. In any case, the proportion of carbon increases the strength and hardenability. In addition to the aforementioned decrease in weldability, machinability
and hot formability also decrease.
|