 Compression Ratio Compression Ratio
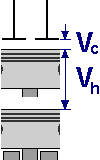
The compression ratio is the relationship of the overall cylinder area before the compression takes place (displacement + cylinder area), to the remaining area after the compression (compression area).
| Higher compression ratio -> higher compresion discharge pressure |
| Higher compression ratio -> higher octane requirement |
The compression can be determined by gauging (incremental filling). To do this, the piston of the cylinder to be measured must be brought to ignition TDC and then filled with a liquid via the spark-plug hole. This can
be done using a syringe whereby, the exact amount, right up to and including the spark-plug thread, is to be noted. The engine is to be placed in a position where the cylinders are vertical, so that no air-bubbles can
develop.
The procedure is then repeated with the piston at BDC. Problems can arise with the proper closing of both valves. This could be achieved by removing the OHC or the rocker-arm(s). Indeed, one could also rely on the
individual cylinder displacement stated by the manufacturer.
Now one only has to subtract the the volume of the spark-plug hole. Perhaps one could immerse an original spark-plug up to the washer in water, then measure the water-level to determine the volume. The final
calculation follows by dividing the two values. (see above). 07/07
cartecc.com
Top of page
Index
2001-2014 Copyright programs, texts, animations, pictures: H. Huppertz - Email
Translator: Don Leslie -
Email: lesdon@t-online.de |