
|
 Cable Restistance Cable Restistance
Cable cross section
in mm² | Continuous current load
(max.) in A |
| 1 | 10 |
| 1,5 | 20 |
| 2,5 | 25 |
| 4 | 35 |
| 6 | 50 |
| 10 | 65 |
| Material | Spec. electr.
Resistance
Ohm·mm²/m |
| Silver | 0,015 |
| Copper | 0,0178 |
| Gould | 0,023 |
| Aluminum | 0,026 |
| Wolfram | 0,049 |
| Platinum | 0,089 |
| Tin | 0,114 |
| Lead | 0,206 |
| Constantan | 0,5 |
The resistance in a solid cable increases with its length and specific resistance and decreases with a larger cross-section. This is the basic formula. In the second formula, only the resistance through the current
strength replaces the voltage drop.
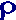 ·l ·l
R=
A |  ·l ·l
A=
R | A·R
l=
 | A·R
 = =
l |
l ·  · I · I
A = 
UA | l ·  · I · I
UA = 
A |
A · UA
I = 
 · l · l | A · UA
l = 
 · I · I |
cartecc.com
Top of page
Index
2001-2014 Copyright programs, texts, animations, pictures: H. Huppertz - Email
Translator: Don Leslie -
Email: lesdon@t-online.de | |

|