
|
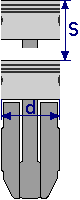
 Stroke to Bore Ratio Stroke to Bore Ratio
| Short stroke, square designed, long-stroke |
The stroke length is compared with the bore diameter. This stroke-bore ratio has an influence on the operational behaviour of the engine. Whereas the short-stroke engine (left picture) has less stroke than bore, with the
long-stroke engine this is (right picture) the other way around. If bore and stroke are approximately the same, one then speaks of an over-square engine.
| Especially short-stroke engines in Formula 1 |
Whereas long-stroke engines provide more torque in the lower RPM range, short-stroke engines are more capable of particularly high revs and large valve openings. An extreme example is the current (2007) Formula 1
engine being a 2,4 Liter-V8 and with about 98 mm of bore and a 40 mm stroke-length.The latter ensures the fact that the average piston speed, despite the maximum
RPM of 19.000 1/min, does not increase the average piston speed much more than 25 m/s. In order to keep the weight of the pistons low, there is no oil ring, almost no piston shaft and a gudgeon pin, which is much
shorter and found directly under the piston crown.
s
s/d = 
d |
|
|